Summary
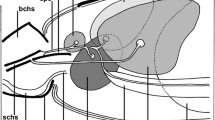
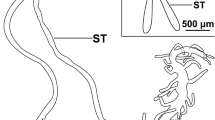
Salivary gland cells of members of theDrosophila melanogaster group (from four different subgroups) were examined electron microscopically and histochemically during the late larval period of development. The secretory product, which is supposed to be utilized as ‘glue’ at the time of puparium formation, appears, by analogy to Palade and Jamieson's results, to be synthesized partially in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) and partially in the Golgi complex. The latter is also the usual site of the packaging of the product into secretory granules, except in the case of one of the secretory granule components ofD. lucipennis. The phylogenetic relationships among the subgroups, implied by the morphological appearance of the secretory granules, fit well with the existing phylogenetic relationships within the group. The secretory granules of each species have their own morphological features; granules of species of the same subgroup share some of these features. Secretion occurs from the cells via exocytosis during which the morphology of the secretory granules changes. Light microscope examination of PAS (Periodic Acid-Schiff reaction) stained glands shows a strong positive reaction in most species, with the exception of the species of thesuzukii subgroup which show a weak, or a negative reaction (D. rajasekari). Electron histochemical localization of polysaccharides in the secretory granules was possible inD. melanogaster and the species of theananassae subgroup.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akam, M.E., Roberts, D.B., Richards, G.P., Ashburner, M.:Drosophila: the genetics of two major larval proteins, Cell13, 215–225 (1978)
Ashhurst, D.E., Costin, N.M.: The secretion of collagen by insects: Uptake of3H-proline by collagen-synthesizing cells inLocusta migratoria andGalleria mellonella. J. Cell Sci.20, 377–403 (1976)
Becker, H.J.: Die Puffs der Speicheldrüsenchromosomen vonDrosophila melanogaster. I. Beobachtungen zum Verhalten des Puffmusters im Normalstamm und bei zwei Mutanten, giant und lethal-giant-larvae. Chromosoma10, 654–678 (1959)
Beermann, W.: Ein Balbiani-ring als Locus Speicheldrüsen-mutation. Chromosoma12, 1–25 (1961)
Bennett, G., Leblond, C.P.: Biosynthesis of the glycoproteins present in plasma membrane, lysosomes and secretory materials as visualized by radioautography. Histochem. J.9, 393–471 (1977)
Berendes, H.D.: Salivary gland function and chromosomal puffing patterns inDrosophila hydei. Chromosoma17, 35–77 (1965)
Berendes, H.D.: The control of puffing inDrosophila hydei. In: Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation. Developmental Studies of Giant Chromosomes (W. Beermann, ed.), Vol. 4, pp. 181–207. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York Springer 1972
Berendes, H.D., Bruyn, W.C., de: Submicroscopic structure ofDrosophila hydei salivary gland cells. Z. Zellforsch.59, 142–152 (1963)
Biiger, W., Seybold, J., Kern, H.F.: Studies on intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the rat exocrine pancreas. V. Kinetic studies on accelerated transport following caerulein infusion in vivo. Cell Tissue Res.170, 203–220 (1976)
Bock, I.R., Wheeler, M.R.: TheDrosophila melanogaster species group. Studies in Geneties VII, 1–102, Univ. Texas Publ. 7213 (1972)
Bodenstein, D.: Factors influencing growth and metamorphosis of the salivary gland inDrosophila. Biol. Bull.84, 13–33 (1943)
Dauwalder, M., Whaley, W.G., Kephart, J.E.: Functional aspects of the Golgi apparatus. Subcell. Biochem.1, 225–276 (1972)
Derksen, J.: Induced RNP production in different cell types ofDrosophila. Cell Differ.4, 1–10 (1975a)
Derksen, J.: The submicroscopic structure of synthetically active units in a puff ofDrosophila hydei giant chromosomes. Chromosoma50, 45–52 (1975b)
Derksen, J.: Ribonuclear protein formation at locus 2-48 C inDrosophila hydei. Nature (London)263, 438–439 (1976)
Derksen, J., Willart, E.: Cytochemical studies on RNP complexes produced by puff 2-48 C inDrosophila hydei. Chromosoma55, 57–68 (1976)
Derksen, J., Berendes, H.D., Willart, E.: Production and release of a locus-specific ribonucleoprotein product in polytene nuclei ofDrosophila hydei. J Cell Biol.59, 661–668 (1973)
Eeken, J.C.J.: Ultrastructure of salivary glands ofDrosophila lebanonensis during normal development and after in vivo ecdysterone administration. J. Insect Physiol.23, 1043–1055 (1977)
Fraenkel, G., Brookes, V.J.: The process by which the puparia of many species of flies become fixed to a substrate. Biol. Bull.105, 442–449 (1953)
Gaudecker, von B.: Der Strukturwandel der Larvalen Speicheldrüse vonDrosophila melanogaster. Ein Beitrag zur Frage nach der Steuerenden Wirkung aktiver gene auf das Cytoplasm. Z. Zellforsch.127, 50–86 (1972)
Gay, H.: Nucleocytoplasmic relations inDrosophila. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol.21, 257–269 (1956)
Grossbach, U.: Chromosomen-Aktivität and Biochemische Zelldifferenzierung in den Speicheldrüsen vonCamptochironomus. Chromosoma28, 136–187 (1969)
Grossbach, U.: Chromosome puffs and gene expression in polytene cells. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol.38, 619–627 (1974)
Grossbach, U.: The salivary gland ofChironomus (Diptera): A model system for the study of cell differentiation. In: Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation. Biochemical Differentiation in Insect Glands. (W. Beermann, ed.) Vol 8, pp. 147–196 Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1977
Haddad, A., Bennett, G., Leblond, C.P.: Formation and turnover of plasma membrane glycoproteins in kidney tubules of young rats and adult mice, as shown by radioautography after an injection of3H-fucose. Am. J. Anat.148, 241–274 (1977)
Harrod, M.J.E., Kastritsis, C.D.: Developmental studies inDrosophila. II. Ultrastructural analysis of the salivary glands ofD. pseudoobscura during some stages of development. J. Ultrastruct. Res.38, 482–499 (1972a)
Harrod, M.J.E., Kastritsis, C.D.: Developmental studies inDrosophila. VI. Ultrastructural analysis of the salivary glands ofD. pseudoobscura during the late larval period. J. Ultrastruct. Res.40, 292–312 (1972b)
Hsu, W.S.: The Golgi material and mitochondria in the salivary glands of the larva ofDrosophila melanogaster Q. J. Microsc. Sci.89, 410–414 (1948)
Jamieson, J.D.: Transport and discharge of exportable proteins in pancreatic exocrine cells: in vitro studies. In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport (F. Bronner, A. Kleinzeller, eds.), Vol. 3, pp. 273–338, London: Academic Press 1972
Jamieson, J.D., Palade, G.E.: Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cells. I. Role of the peripheral elements of the Golgi complex. J. Cell Biol.34, 577–596 (1967a)
Jamieson, J.D., Palade, G.E.: Intracellular transport of secretory proteins in the pancreatic exocrine cells. II. Transport to condensing vacuoles and zymogen granules. J. Cell Biol.34, 597–615 (1967b)
Jamieson, J.D., Palade, G.E.: Synthesis, intracellular transport and discharge of secretory proteins in stimulated pancreatic exocrine cells. J. Cell Biol.50, 135–158 (1971)
Karnovsky, M.J.: A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolatity for use in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.27, 137a (1965)
Bartenbeck, J., Franke, W.W.: Membrane relationships between endoplasmic reticulum and peroxisomes in rat hepatocytes and Morris hepatoma cells. Cytobiologie10, 152–156 (1974)
Kessel, R.G.: Origin of the Golgi apparatus in embryonic cells of the grasshopper. J. Ultrastruct. Res.34, 260–275 (1971)
Kloetzel, J.A., Laufer, H.: A fine structural analysis of larval salivary gland function inChironomus thummi. J. Ultrastruct. Res.29, 15–36 (1969)
Korge, G.: Chromosome puff activity and protein synthesis in larval salivary glands ofDrosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA72, 4550–4554 (1975)
Korge, G.: Direct correlation between a chromosome puff and the synthesis of a larval saliva protein inDrosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma62, 155–174 (1977a)
Korge, G.: Larval saliva inDrosophila melanogaster. Production, composition and relationship to chromosome puffs. Dev. Biol.58, 339–355 (1977b)
Kress, H.: Specific regression of a puff in the salivary gland chromosomes ofDrosophila virilis after injection of glucosamine. Chromosoma40, 379–386 (1973)
Lane, N.J., Carter, Y.R., Ashburner, M.: Puffs and salivary gland function: The fine structure of the larval and prepupal salivary glands ofDrosophila melanogaster. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwicklungsmech. Org.169, 216–238 (1972)
Leenders, H.J., Derksen, J., Maas, P.M.J.M., Berendes, H.D.: Selective induction of a giant puff inDrosophila hydei by vitamin B6 and derivatives. Chromosoma41, 447–460 (1973)
MacGregor, H.C., Mackie, J.B.: Fine structure of the cytoplasm in salivary glands ofSimulium. J. Cell Sci.2, 137–144 (1967).
Morré, D.J.: Membrane differentiation and the control of secretion: A comparison of plant and animal Golgi apparatus. In: International Cell Biology (B.R. Brinkley, K.R. Porter, eds.), pp. 293–303. New York: Rockefeller Univ. Press 1976–1977
Morré, D.J., Mollenhauer, H.H.: The endomembrane concept: a functional integration of endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus. In: Dynamic Aspects of Plant Ultrastructure (A.W. Robards, ed.), pp. 84–137, New York: McGraw Hill 1974
Morré, D.J., Mollenhauer, H.H., Bracker, C.E.: Origin and continuity of Golgi apparatus. In: Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation. II. Origin and Continuity of Cell Organelles (J. Reinert, H. Ursprung, eds.), pp. 82–126. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag 1971
Ohba, S.: Analytical studies on the experimental population ofDrosophila. I. The effect of larval population density upon the preadult growth ofDrosophila melanogaster andDrosophila virilis, with special reference to their nutritional conditions. Okayama Univ. Biol. J.7, 87–125 (1961)
Okretic, M.C., Penoni, J.S., Lara, F.J.S.: Messenger-like RNA synthesis and DNA chromosomal puffs in the salivary gland ofRhynchosciara americana. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.178, 158–165 (1977)
Painter, T.S.: Nuclear phenomena associated with secretion in certain gland cells with especial reference to the origin of cytoplasmic ribonucleic acid. J. Exp. Zool.100, 523–547 (1946)
Palade, G.E.: The secretory process of the pancreatic exocrine cells. In: Electron Microscopy in Anatomy (J.D. Boyd, F.R. Johnson, J.D. Lever, eds.), Baltimore: Wilkins and Wilkins Co. 1961
Palade, G.E.: Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science189, 347–358 (1975)
Pasteur, N., Kastritsis, C.D.: Developmental studies inDrosophila. I. Acid phosphatases esterases and other proteins in organs and whole-fly homogenates during development ofD. pseudoobscura. Dev. Biol.26, 525–536 (1971)
Pasteur, N., Kastritsis, C.D.: Developmental studies inDrosophila. IV. Quantitative protein changes in organs and whole-fly homogenates during development ofD. pseudoobscura. Experientia28, 215–216 (1972)
Pasteur, N., Kastritsis, C.D.: Developmental studies inDrosophila. V. Alkaline phosphatases, dehydrogenases and oxidases in organs and whole-fly homogenates during development ofD. pseudoobscura. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwicklungsmech. Org.173, 346–354 (1973)
Pearse, A.G.E.: Histochemistry-Theoretical and Applied. Vol 1, 3rd edn. Edinburgh-Harlow: Churchill Livingstone 1968
Phillips, D.M., Swift, H.: Cytoplasmic fine structure ofSciara salivary glands. J. Cell Biol.27, 395–409 (1965)
Poels, C.L.M.: Mucopolysaccharide secretion fromDrosophila salivary gland cells as a consequence of hormone induced gene activity. Cell Differ.1, 63–76 (1972)
Poels, C.L.M., Loof, A. de, Berendes, H.D.: Functional and structural changes inDrosophila salivary gland cells triggered by ecdysterone. J. Insect Physiol.17, 1717–1729 (1971)
Price, N.C., Hunt, S.: An unusual type of secretory cell in the ventral pedal gland of the gastropod molluscBuccinum undatum L. Tissue & Cell8, 217–228 (1976)
Rambourg, A.: An improved silver methenamine technique for the detection of periodic acid-reactive complex carbohydrates with the electron microscopy. J. Histochem. Cytochem.15, 409–412 (1967)
Rambourg, A., Hernandez, W., Leblond, C.D.: Detection of periodic acid-reactive carbohydrate in Golgi saccules. J. Cell Biol.40, 395–414 (1969)
Reynolds, E.S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol.17, 208–218 (1963)
Rizki, T.M.: Ultrastructure of the secretory inclusions of the salivary gland cells inDrosophila. J. Cell Biol.32, 531–534 (1967)
Ronzio, R.A., Mohrlok, S.H.: A possible role of Golgi membrane-associated galactosyl-transferase in the formation of zymogen granule glycoproteins. Arch. Biochem. Biophys.181, 128–136 (1977)
Ross, E.B.: The post-embryonic development of the salivary glands ofDrosophila melanogaster J. Morphol.64, 471–495 (1939)
Rougier, M.: Secretion de polysaccharides dans l'apex radiculaire de mais: etude radioautographique par incorporation de fucose tritie. J. Microsc. Biol. Cellul.26, 161–166 (1976)
Satir, B.: The final steps in secretion. Sci. Am.233, 28–37 (1975)
Spurr, A.R.: A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res.26, 31–43 (1969)
Stocker, A.J., Jackson, J.: A technique for the synchronization ofDrosophila for developmental studies. D.I.S.46, 157 (1971)
Stocker, A.J., Kastritsis, C.D.: Developmental studies inDrosophila. III. The puffing patterns of the salivary gland chromosomes ofD. pseudoobscura. Chromosoma37, 139–176 (1972)
Stocker, A.J., Kastritsis, C.D.: Developmental studies inDrosophila. 7. The influence of ecdysterone on the salivary gland puffing patterns ofD. pseudoobscura larvae and prepupae. Differentiation1, 225–239 (1973)
Sturgess, J.M. de la, Iglesia, F.A., Minaker, E., Mitranic, M., Moscarello, M.A.: The Golgi complex. II. The effects of aminonucleoside on ultrastructure and glycoprotein biosynthesis. Lab. Invest.31, 6–14 (1974)
Swift, H.: Nucleic acids and cell morphology in Dipteran salivary glands. In: The Molecular Control of Cellular Activity (J.M. Allen, ed.), pp. 73–125. New York: McGraw Hill 1962
Swift, H.: Molecular morphology of the chromosome. In: The Chromosomes In Vitro (G. Gregarian, ed.), Vol. 1, pp. 26–49, Baltimore: The Williams and Wilkins Co. 1965
Thiery, J.P.: Role de l'appareil de Golgi dans la synthese des mucopolysaccharides: etude cytochimique. Mise en evidence de mucopolysaccharides dans les saccules de transition entre l'ergastoplasme et l'appareil de Golgi. J. Microsc.8, 689–708 (1969)
Vidal, O.R., Spirito, S., Riva, R.: Heterogenous ultrastructure of the granules ofDrosophila salivary glands. Experientia27, 178–179 (1970)
Weston, J.C., Ackerman, G.A., Greider, M.H., Nikolewski, R.F.: Nuclear membrane contributions to the Golgi complex. Z. Zellforsch.123, 153–160 (1972)
Whaley, W.G.: The Golgi apparatus. In: Cell Biology Monograph, 2. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer 1975
Whaley, W.G., Dauwalder, M., Kephart, J.E.: Assembly, continuity and exchanges in certain cytoplasmic membrane systems. In: Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation. Origin and Continuity of Cell Organelles (J. Reinert, H. Ursprung, eds.), Vol 2, pp. 1–45. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York Springer 1971
Winter, C.E., Bianchi, A.G. de, Terra, W.R., Lara, F.J.S.: Relationships between newly synthesized proteins and DNA puff patterns in salivary glands ofRhynchosciara americana. Chromosoma61, 193–206 (1977)
Wise, G.E.: Connections between cisternae of the Golgi apparatus and the granular endoplasmic reticulum in Amoeba proteus. Z. Zellforsch.126, 431–436 (1972)
Zhimulev, I.F., Kolesnikof, N.N.: Synthesis and secretion of mucoprotein glue in the salivary gland ofDrosophila melanogaster. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwicklungsmech. Org.178, 15–28 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomopoulos, G.N., Kastritsis, C.D. A comparative ultrastructural study of ‘glue’ production and secretion of the salivary glands in different species of theDrosophila melanogaster group. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv 187, 329–354 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00848468
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00848468