Abstract
This open study evaluated the influence of renal function on the pharmacokinetics of ranitidine (50 mg iv infusion given over 6 min). Five groups, each of 8 subjects, 1 with normal renal function and 4 with different degrees of renal impairment were studied.
Renal function was assessed in each patient by 51Cr-EDTA (glomerular filtration rate, GFR), creatinine clearance (GFR) and N-methylnicotinamide clearance (reflecting glomerular and tubular function). Sixteen blood samples (5 ml) taken up to 48 h post dose from each subject were analysed for plasma ranitidine concentrations by reversed phase HPLC.
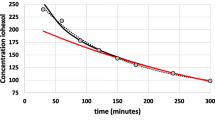
Patient groups with renal impairment had significantly increased AUC∞ and t1/2 with corresponding decreases in CLp and λz when compared with normal subjects. There was also a significant increase in tmax but not in Cmax. There was a high linear correlation between the degree of renal impairment and ranitidine clearance.
In patients with GFR ≤ 20 ml min−1, the AUC∞ mean ratio (compared with normal subjects) was up to 4.6 while for patients with GFR 20–50 ml min−1, the average AUC∞ ratio was 2.6. It is recommended that the dose of ranitidine is halved in patients with GFR ≤ 20 ml min−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garg DC, Baltodano N, Jallad NS, Perez G, Oster JR, Eshelman FN, Weidler DJ (1986) Pharmacokinetics of ranitidine in patients with renal failure. J Clin Pharmacol 26: 286–291
Zech PY, Chau NP, Pozet N, Labeauw M, Hadj-Aissa A (1983) Ranitidine kinetics in chronic renal impairment. Clin Pharmacol Ther 34: 667–672
Meffin PJ, Grgurnovich N, Brooks PM, Miners JO, Cochran M, Stranks G (1983) Ranitidine disposition in patients with renal impairment. Br J Clin Pharmacol 16: 731–734
McFadyen LM, Folb PI, Miller R, Keeton GR, Marks IN (1983) Pharmacokinetics of ranitidine in patients with chronic renal failure. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 25: 347–351
Kopitar Z, Cuelbar P, Zorz M (1987) Pharmacokinetics of ranitidine in adult patients with end stage renal disease after single and multiple dosing. Acta Pharm Jugosol 37: 371–379
Gladziwa U, Klotz U (1993) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of H2-receptor antagonists in patients with renal insufficiency. Clin Pharmacokinet 24: 319–332
Bricker NS (1969) On the meaning of the intact nephron hypothesis. Am J Med 46: 1–11
Maiza A, Daley-Yates PT (1988) The clearance of drugs in different types of renal disease. Renal Failure 11: 67
Cockroft DW, Gault MH (1976) Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 16: 31–41
Clark BR, Halpern RM, Smith RA (1975) A fluorimetric method for quantification in the picomole range of N-methylnicotinamide and nicotinamide in serum. Anal Biochem 68: 54–61
Shim CK, Sawada Y, Iga T, Honano M (1984) Estimation of renal secretory function for organic cations by endogenous N-methylnicotinamide in rats with experimental renal failure. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 12: 23–42
Cartwright AC (1991) Barcelona Drug Information Association Workshop International Consensus Statement on Bioavailability/Bioequivalence testing requirements and standards. Drug Info J 25: 473–482
Kruskal WH, Wallis WA (1952) Use of ranks on one-criterion variance analysis. Am Stat Assoc 47: 583–621
Hodges JL Jr, Lehmann EL (1963) Estimates of location based on rank tests. Ann Math Stats 34: 598–611
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dixon, J.S., Borg-Costanzi, J.M., Langley, S.J. et al. The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics of ranitidine. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 46, 167–171 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199883
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199883