Abstract
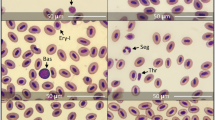
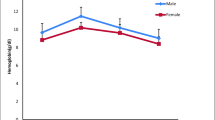
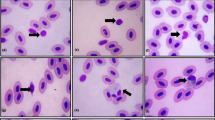
Certain blood morphology parameters: red blood cell (RBC) sizes; percentage of polymorphonuclear leukocytes and ratio polychromatocyte/RBC in Brown trout (Salmo trutta L.) from acidified water (mean pH value 4.94) and limed water (mean pH value 5.66) were investigated. The sizes of RBC long axises were significantly larger in fish from acidic environment than from limed condition (14.37 and 12.96μm respectively). The percentage of polymorphonuclear cells (7.86 and 3.32) and polychromatocyte/RBC ratio (0.079 and 0.019) were also significantly larger in fish from the acidified environment. Blood morphology parameters are concluded to be usefull for testing and detection of long-term acidic stress in fish in nature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blaxhall, P. C. and Daisely, K. W.: 1973,J. Fish. Biol. 5, 711–781.
Cameron, J. N.: 1989,Acid Toxicity and Aquatic Animals, Cambridge University Press, pp. 99–112.
DN-report 1993–1994: 1994,Monitoring of Lakes and Rivers in Norway, Trondheim, Norway, pp. 74–75.
DN-report 1994–1995: 1995,Monitoring of Lakes and Rivers in Norway, Trondheim, Norway (in press).
Eriksson, F., Hörnström, E., Mossberg, P. and Nyberg, P.: 1983,Hydrobiologia 101, 145–164
Fromm, P. O.: 1980,Envir. Biol. Fish 5, 79–93.
Fugelli, K. and Vislie, T.: 1982,J. Exp. Biol. 101, 71–82.
Giles, M. A., Majewski, H. S. and Hobden, B.: 1984,Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 41, 1686–1694.
Heisler, N.: 1986,Acid Toxicity and Aquatic Animals, Cambridge University Press, pp. 85–97.
Holopainen, I. J. and Oikari, A.: 1992,Annales Zoological Fennici 29(1), 29–28.
Ivanova, N. T.: 1982,Atlas krovi ryb, ed. Pischevaya prom., Rostov, 236.
Leino, R. L. and McCormick, J. H.: 1993,Can. J. of Zoology 71(3), 531–543.
Mason, J.: 1989,Acidic Toxicity and Aquatic Animals, Cambridge University Press, 1–2.
Matei, V. E. and Komov, V. T.: 1993,Zhurnal Evolyutsionnoi biokhimii i fiziologii 28(5), 596–604.
Milligan, C. L. and Wood, C. M.: 1982,J. Exp. Biol. 99, 397–415.
Reader, J. R. and Dempsey, C. H.: 1989,Acid Toxcicity and Aquatic Animals, Cambridge University Press, pp. 67–85.
Rosseland, B. O., Skogheim, K. O., Abrahamsen, H. and Matzow, D.: 1986,Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 43, 1888–1893.
Van Dijk, P. L., Van Den Thillart, G. E., Balm, P. and Bonga, S. W.:Journ. of Fish. Biol. 42(5), 661–671.
Wood, C. M. and McDonald, D. G.: 1982,Acid Rain/Fisheries, R. E. Johnson (ed.), Bethesda:Am. Fish. Soc., pp. 197–226.
Wood, C. M., Playle, R. C., Simons, B. P., Gross, G. G. and McDonald, D. G.: 1988a,Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 45, 1575–1576.
Wood, C. M., McDonald, D. G., Booth, C. E., Simons, B. P., Ingersol, C. G. and Bergman, H. L.: 1988b,Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 45, 1587–1596.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galina, M.S. The difference in brown trout (Salmo Trutta L.) blood composition from acidic and limed sites of two rivers in Western Norway. Water Air Soil Pollut 96, 203–210 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407205
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02407205