Summary
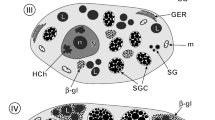
The ultrastructure of hepatic peroxisomes was investigated in Ichthyophis glutinosus (Amphibia: Gymnophiona), employing perfusion fixation and the diaminobenzidine (DAB) technique for the visualization of catalase. The majority of peroxisomes is circular or rod-shaped, although elongated particles occasionally occur. They contain a finely granular matrix, lightly stained after the DAB procedure. Their mean diameter is approximately 0.25 μm. Serial sections reveal that the circular and rod-shaped peroxisomal profiles are cross and oblique sections of highly tortuous, tubular organelles exceeding 2 μm in length.
In addition to tubular profiles, elongated, rectangular particles, as well as straight dumbbell-shaped organelles with distinct marginal plates are observed. They range from 900 to 1650 nm in length (mean = 1200 nm). In the flattened, thin central portion of the dumbbell-shaped particle, the peroxisomal membranes form a cisterna enclosing one or two uniformly thick marginal plates, which display a definite substructure with a periodicity of 10 nm.
These findings indicate that peroxisomes in the liver of Ichthyophis exhibit a complex organization. It is suggested that the organelles undergo a specific differentiation process, morphologically characterized by the formation of enlarged segments of unusual shape.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böck P, Kramar R, Pavelka M (1980) Peroxisomes and related particles in animal tissues. Cell Biol Monogr 7. Springer, Wien New York
Dauca M, Calvert R, Ménard D, Hugon JS, Hourdry J (1982) Development of peroxisomes in amphibians. II. Cytochemical and biochemical studies on the liver, kidney, and pancreas. J Exptl Zool 223:57–65
Dauca M, Calvert R, Ménard D, Hugon JS, Hourdry J (1983) Development of peroxisomes in amphibians. III. Study on liver, kidney, and intestine during thyroxine-induced metamorphosis. J Exptl Zool 227:413–422
Gorgas K (1982) Serial section analysis of peroxisomal shape and membrane relationships in the mouse preputial gland. In: Kindl H, Lazarow PB (eds) Peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. Ann NY Acad Sci 386:519–522
Gorgas K (1984) Peroxisomes in sebaceous glands. V. Complex peroxisomes in the mouse preputial gland: Serial sectioning and three-dimensional reconstruction studies. Anat Embryol 169:261–270
Gorgas K, Zaar K (1984) Peroxisomes in sebaceous glands. III. Morphological similarities of peroxisomes with smooth endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi stacks in the circumanal gland of the dog. Anat Embryol 169:9–20
Hruban Z, Rechcigl M (1969) Microbodies and related particles. Acad Press, New York London
Jones RG, Davis WL, Goodman DBP (1981) Microperoxisomes in the epithelial cells of the amphibian urinary bladder: An electron microscopic demonstration of catalase and malate synthase. J Histochem Cytochem 29:1150–1156
Karnovsky MJ (1971) Use of ferrocyanide-reduced osmium tetrox-ide in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol: Abstr 284
LeHir M, Herzog V, Fahimi HD (1979) Cytochemical detection of catalase with 3,3′-diaminobenzidine. A quantitative reinvestigation of the optimal conditions. Histochemistry 64:51–66
Reddy J, Svoboda D (1973) Microbody (peroxisome) matrix: transformation into tubular structures. Virchows Arch B Zellpath 14:83–92
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208–229
Richardson KC, Jarett L, Finke EH (1960) Embedding in epoxy resins for ultrathin sectioning in electron microscopy. Stain Technol 35:313–325
Roels F, Schiller B, Goldfischer S (1970) Microbodies (peroxi-somes) in the toad, Bufo marinus.A Cytochemical study. Z Zellforsch 108:139–149
Scott PJ, Visentin LP, Allen JM (1969) The enzymatic characteristics of peroxisomes of amphibian and avian liver and kidney. Ann NY Acad Sci 169:244–264
Visentin LP, Allen JM (1969) Allantoinase: Association with amphibian hepatic peroxisomes. Science 163:1463–1464
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, Fa 146/1-2 and Sto 75/9
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gorgas, K., Storch, V. Marginal plates in hepatic peroxisomes of Ichthyophis glutinosus (Amphibia: Gymnophiona). Cell Tissue Res. 238, 413–416 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217316
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00217316