Abstract
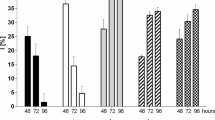
The flagellate alga Pavlova viridis Tseng was investigated in the laboratory for accumulation of the heavy metals, silver, cadmium, cobalt, copper, mercury, nickel and lead. The cultures were grown in an artificial seawater medium mixed with the individual metals at different concentrations. Based on data from the controls, the baseline metal concentrations in P. viridis were shown to be in an order of Cu > Pb > Co > Cd > Ni > Ag > Hg. In the experimental groups, the seven metals displayed different isotherm equilibrium patterns and the metal uptake capacity of the alga was Ni > Pb > Co > Hg > Cu > Cd > Ag at equilibrium. When assessed using the bioconcentration factors, metal accumulation by P. viridis was demonstrated to be the most efficient at a concentration of 0.001 mg L-1 for Ag, Cd and Co, and at 0.01 mg L-1 for Cu, Hg, Ni and Pb. This study suggests that P. viridis can be a source of mineral supplements in mariculture. The alga is not, however, recognized as an effective agent for removing heavy metals from wastewater.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown MR, Jeffrey SW, Garland CD (1989) Nutritional Aspects of Microalgae Used in Mariculture; A Literature Review. CSIRO Marine Laboratories Report 205, CSIRO, Australia.
Drba K, Véber K, Zahradnik J (1985) Toxicity and accumulation of copper and cadmium in the alga Scenedesmus obliquusLH. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxicol. 34: 904-908.
Eisler R (1981) Trace Metal Concentrations in Marine Organisms. Pergamon Press, New York.
Fabregas J, Herrero C (1986) Marine microalgae as potential source of minerals in fish diets. Aquaculture 51: 237-243.
Mao D (1996) Investigations of Optimum Conditions for the Growth ofPavlova viridisTseng in Laboratory and the Production of Eicosapentaenoic Acid in the Alga via Fermentation. M. Phil. thesis, Fujian Normal University.
National Environmental Protection Department, People's Republic of China (1988) Integrated wastewater discharge standard. In: The Laws and Policies for Environmental Protection Vol 2. Fujian Provincial Environmental Protection Department, Fuzhou: 392-395.
Ogino C, Yang GY (1980) Requirements of carp and rainbow trout for dietary manganese and copper. Bull. Jpn. Soc. Sci. Fish. 46: 455-458.
Okuda Y, Mizutani M, Ogawa M, Sone H, Asano M, Asakura Y, Isaka M, Suzuki S, Kawakami Y, Field JB, Yamashita K (1996) Long-term effects of eicosapentaenoic acid on diabetic peripheral neuropathy and serum lipids in patients with type II diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Compl. 10: 280-287.
Riley JP, Roth I (1971) The distribution of trace elements in species of phytoplankton grown in culture. J. mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 51: 63-72.
Sadiq M (1992) Toxic Metal Chemistry in Marine Environments. Marcel Dekker, New York.
Sakaguchi T, Tsuji T, Nakajima A, Horikoshi T (1979) Studies on the accumulation of heavy metal elements in biological systems. XIV. Accumulation of cadmium by green microalgae. Eur. J. appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 8: 207-215.
Sandau E, Sandau, P, Pulz O, Zimmermann M (1996a) Heavy metal sorption by marine algae and algal by-products. Acta Biotechnol. 16: 103-119.
Sandau E, Sandau P, Pulz O (1996b) Heavy metal sorption by microalgae. Acta Biotechnol. 16: 227-235.
Schjott J, Brurok H, Jynge P, Bjerve KS (1996) Effects of eicosapentaenoic acid and decosahexaenoic acid diet supplement on tolerance to the cardiotoxicity of epirubicin and to ischaemia reperfusion in the isolated rat heart. Pharm. Tox. 79: 65-72.
Schulz-Baldes M, Lewin RA (1976) Lead uptake in two marine phytoplankton organisms. Biol. Bull. 150: 118-127.
Skjak G, Jensen A (1976) Heavy metal tolerance of marine phytoplankton. III. Combined effects of copper and zinc ions on cultures of four common species. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 225: 37-50.
Stanley JG, Jones JB (1976) Feeding algae to fish. Aquaculture 7: 219-223.
Wilde EW, Benemann J (1993) Bioremoval of heavy metals by the use of microalgae. Biotech. Adv. 11: 781-812.
Wong PK, Chang L (1991) Effects of copper, chromium and nickel on growth, photosynthesis and chlorophyll asynthesis of Chlorella pyrenoidosa251. Envir. Pollut. 72: 127-139.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Bl., Huang, Q., Lin, Xj. et al. Accumulation of Ag, Cd, Co, Cu, Hg, Ni and Pb in Pavlova viridis Tseng (Haptophyceae). Journal of Applied Phycology 10, 371–376 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008048410419
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008048410419