Abstract
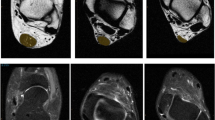
We studied a xanthomatous Achilles tendon and a normal Achilles tendon with the proton magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and spectroscopy (MRS) at 1.5 T in a standard head coil. TheT 2 maps and the localized proton spectra of the Achilles tendon were reconstructed. The normal tendon revealed no MR signal, whereas the xanthomatous tendon image consisted of variable signal intensities, for which the value ofT 2 was significantly shorter (p=0.0002) than that of adipose tissue. The proton spectrum of this tendon xanthoma showed an increased water peak and unsaturated olefinic group intensity compared with the spectrum of the normal Achilles tendon area. The complex cholesterol molecule itself cannot be proven directly in a xanthomatous tendon, but its presence can be revealed with the help of the increased methyl and methylene groups of the fatty acids of the cholesteryl esters. This and other typical features describedin vitro for atheromatous tissue can be detectedin vivo in xanthomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto A, Kamiya T, Yamamura T, Yokoyama S, Yasunori H, Funahashi T, Kawaguchi A, Miyake Y, Beppu S, Ishikawa K, Matsuzawa Y, Takaichi S (1989) Clinical features of familial hypercholesterolemia.Arteriosclerosis 9(Suppl. 1): 66–74.
Liem M, Gevers Leuven J, Bloem J, Schipper J (1992) Magnetic resonance imaging of Achilles tendon xanthomas in familial hypercholesterolemia.Skeletal Radiol 21 453–457.
Kamman RL, Go KG, Muskiet FAJ, Stomp Gp, Van Dijk P, Berendsen HJC (1984) Proton spin relaxation studies of fatty tissue and cerebral white matter.Magn Reson Imaging 2 211–220.
Odeblad E, Lindstrom G (1955) Some preliminary observations on the PMR in biological samples.Ada Radiol 43 469–476.
Kruth HS (1985) Lipid deposition in human tendon xanthoma.Am J Pathol 121 312–314.
Bhattacharyya AK, Connor WE, Mauslof FA, Flatt AE (1976) Turnover of xanthoma cholesterol in hyperlipoproteinemia patients.J Lab Clin Med 87 503–518.
Maynor C, Charles C, Herfkens R, Suddarth S, Johnsson G (1989) Chemical shift imaging of atherosclerosis at 7.0 Tesla.Invest Radiol 24 52–60.
Baes H, van Gent CM, Pries C (1968) Lipid composition of various types of xanthoma.J Invest Dermatol 51 286–293.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Additional reprints of this chapter may be obtained from the Reprints Department, Chapman & Hall, One Penn Plaza, New York, NY 10119.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koivunen-niemelä, T., Komu, M., Viikari, J. et al. Mri and mrs of human tendon xanthoma at 1.5 t: Anin vivo study. MAGMA 2, 121–126 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01753068
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01753068