Abstract
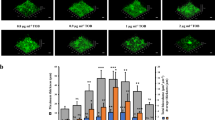
Bacterial biofilms are an important cause of nosocomial infections. Microorganisms such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa colonize biotic and abiotic surfaces leading to chronic infections that are difficult to eradicate. To characterize novel genes involved in biofilm formation, we identified the lpxD gene from a transposon-mutant library of P. aeruginosa. This gene encodes a glucosamine-N acyltransferase, which is important for lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis. Our results showed that a loss-of-expression mutant of lpxD was defective for biofilm formation on biotic and abiotic surfaces. Additionally, this mutant strain exhibited significantly decreased bacterial attachment to cultured airway epithelial cells, as well as increased bacterial cytotoxicity toward airway cells. However, consistent with a defect in lipid A structure, airway cells incubated with the lpxD mutant or with mutant lipid A extracts exhibited decreased IL-8 production and necrosis, respectively. Overall, our data indicate that manipulating lpxD expression may influence P. aeruginosa’s ability to establish biofilm infections.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson GG, Moreau-Marquis S, Stanton BA, O’Toole GA (2008) In vitro analysis of tobramycin-treated Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms on cystic fibrosis-derived airway epithelial cells. Infect Immun 76:1423–1433
Anderson GG, Yahr TL, Lovewell RR, O’Toole GA (2010) The Pseudomonas aeruginosa magnesium transporter MgtE inhibits transcription of the type III secretion system. Infect Immun 78:1239–1249
Augustin DK et al (2007) Presence or absence of lipopolysaccharide O antigens affects type III secretion by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 189:2203–2209
Badger J et al (2011) The structure of LpxD from Pseudomonas aeruginosa at 1.3 A resolution. Acta Crystallogr, Sect F: Struct Biol Cryst Commun 67:749–752
Beutler B, Cerami A (1988) Tumor necrosis, cachexia, shock, and inflammation: a common mediator. Annu Rev Biochem 57:505–518
Beveridge TJ, Makin SA, Kadurugamuwa JL, Li Z (1997) Interactions between biofilms and the environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev 20:291–303
Bodewits K, Raetz CR, Govan JR, Campopiano DJ (2010) Antimicrobial activity of CHIR-090, an inhibitor of lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis, against the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 54:3531–3533
Buetow L, Smith TK, Dawson A, Fyffe S, Hunter WN (2007) Structure and reactivity of LpxD, the N-acyltransferase of lipid A biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:4321–4326
Chen HC et al (2004) Neutrophil elastase induces IL-8 synthesis by lung epithelial cells via the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Biomed Sci 11:49–58
Clementz T, Zhou Z, Raetz CR (1997) Function of the Escherichia coli msbB gene, a multicopy suppressor of htrB knockouts, in the acylation of lipid A. Acylation by MsbB follows laurate incorporation by HtrB. J Biol Chem 272:10353–10360
Coburn B, Sekirov I, Finlay BB (2007) Type III secretion systems and disease. Clin Microbiol Rev 20:535–549
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322
Cryz SJ Jr, Pitt TL, Furer E, Germanier R (1984) Role of lipopolysaccharide in virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun 44:508–513
Davey ME, O’Toole GA (2000) Microbial biofilms: from ecology to molecular genetics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:847–867
Doring G, Parameswaran IG, Murphy TF (2011) Differential adaptation of microbial pathogens to airways of patients with cystic fibrosis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35:124–146
Drewniak A, Tool AT, Geissler J, van Bruggen R, van den Berg TK, Kuijpers TW (2010) Toll-like receptor-induced reactivity and strongly potentiated IL-8 production in granulocytes mobilized for transfusion purposes. Blood 115:4588–4596
El Hamidi A, Tirsoaga A, Novikov A, Hussein A, Caroff M (2005) Microextraction of bacterial lipid A: easy and rapid method for mass spectrometric characterization. J Lipid Res 46:1773–1778
Ernst RK et al (1999) Specific lipopolysaccharide found in cystic fibrosis airway Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Science 286:1561–1565
Fink SL, Cookson BT (2005) Apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necrosis: mechanistic description of dead and dying eukaryotic cells. Infect Immun 73:1907–1916
Friedman L, Kolter R (2004) Genes involved in matrix formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 biofilms. Mol Microbiol 51:675–690
Galanos C, Freudenberg MA (1993) Mechanisms of endotoxin shock and endotoxin hypersensitivity. Immunobiology 187:346–356
Gibson RL, Burns JL, Ramsey BW (2003) Pathophysiology and management of pulmonary infections in cystic fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:918–951
Gon Y et al (2004) A20 inhibits toll-like receptor 2- and 4-mediated interleukin-8 synthesis in airway epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 31:330–336
He W et al (2013) LPS induces IL-8 expression through TLR4, MyD88, NF-kappaB and MAPK pathways in human dental pulp stem cells. Int Endod J 46:128–136
Kanipes MI, Lin S, Cotter RJ, Raetz CR (2001) Ca2+ -induced phosphoethanolamine transfer to the outer 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid moiety of Escherichia coli lipopolysaccharide. A novel membrane enzyme dependent upon phosphatidylethanolamine. J Biol Chem 276:1156–1163
Kuchma SL, Connolly JP, O’Toole GA (2005) A three-component regulatory system regulates biofilm maturation and type III secretion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 187:1441–1454
Kulshin VA, Zahringer U, Lindner B, Jager KE, Dmitriev BA, Rietschel ET (1991) Structural characterization of the lipid A component of Pseudomonas aeruginosa wild-type and rough mutant lipopolysaccharides. Eur J Biochem 198:697–704
Liberati NT et al (2006) An ordered, nonredundant library of Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PA14 transposon insertion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:2833–2838
McIntire CR, Yeretssian G, Saleh M (2009) Inflammasomes in infection and inflammation. Apoptosis 14:522–535
Musken M, Di Fiore S, Dotsch A, Fischer R, Haussler S (2010) Genetic determinants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm establishment. Microbiology 156:431–441
O’Toole GA, Kolter R (1998a) Flagellar and twitching motility are necessary for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Mol Microbiol 30:295–304
O’Toole GA, Kolter R (1998b) Initiation of biofilm formation in Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 proceeds via multiple, convergent signalling pathways: a genetic analysis. Mol Microbiol 28:449–461
O’Toole GA, Pratt LA, Watnick PI, Newman DK, Weaver VB, Kolter R (1999) Genetic approaches to study of biofilms. Methods Enzymol 310:91–109
O’Toole GA, Gibbs KA, Hager PW, Phibbs PV Jr, Kolter R (2000) The global carbon metabolism regulator Crc is a component of a signal transduction pathway required for biofilm development by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 182:425–431
Raetz CR, Whitfield C (2002) Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem 71:635–700
Raetz CR, Reynolds CM, Trent MS, Bishop RE (2007) Lipid A modification systems in gram-negative bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem 76:295–329
Rietschel ET et al (1994) Bacterial endotoxin: molecular relationships of structure to activity and function. FASEB J 8:217–225
Ryder C, Byrd M, Wozniak DJ (2007) Role of polysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm development. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:644–648
Sauer K, Camper AK, Ehrlich GD, Costerton JW, Davies DG (2002) Pseudomonas aeruginosa displays multiple phenotypes during development as a biofilm. J Bacteriol 184:1140–1154
Shanks RM, Caiazza NC, Hinsa SM, Toutain CM, O’Toole GA (2006) Saccharomyces cerevisiae-based molecular tool kit for manipulation of genes from gram-negative bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5027–5036
Simon R, Quandt J, Klipp W (1989) New derivatives of transposon Tn5 suitable for mobilization of replicons, generation of operon fusions and induction of genes in gram-negative bacteria. Gene 80:161–169
Somerville JE Jr, Cassiano L, Bainbridge B, Cunningham MD, Darveau RP (1996) A novel Escherichia coli lipid A mutant that produces an antiinflammatory lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest 97:359–365. doi:10.1172/JCI118423
Vaara M (1993) Antibiotic-supersusceptible mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 37:2255–2260
Vaara M, Nurminen M (1999) Outer membrane permeability barrier in Escherichia coli mutants that are defective in the late acyltransferases of lipid A biosynthesis. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:1459–1462
Valvano MA (2003) Export of O-specific lipopolysaccharide. Front Biosci 8:s452–s471
Ventre I et al (2006) Multiple sensors control reciprocal expression of Pseudomonas aeruginosa regulatory RNA and virulence genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:171–176
Vuorio R, Vaara M (1992) Mutants carrying conditionally lethal mutations in outer membrane genes omsA and firA (ssc) are phenotypically similar, and omsA is allelic to firA. J Bacteriol 174:7090–7097
Wang X, Quinn PJ (2010) Lipopolysaccharide: biosynthetic pathway and structure modification. Prog Lipid Res 49:97–107
Winsor GL et al (2011) Pseudomonas Genome Database: improved comparative analysis and population genomics capability for Pseudomonas genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 39:D596–D600
Wolfgang MC, Lee VT, Gilmore ME, Lory S (2003) Coordinate regulation of bacterial virulence genes by a novel adenylate cyclase-dependent signaling pathway. Dev Cell 4:253–263
Xavier JB, Kim W, Foster KR (2011) A molecular mechanism that stabilizes cooperative secretions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 79:166–179
Zhou Z, Ribeiro AA, Lin S, Cotter RJ, Miller SI, Raetz CR (2001) Lipid A modifications in polymyxin-resistant Salmonella typhimurium: PMRA-dependent 4-amino-4-deoxy-L-arabinose, and phosphoethanolamine incorporation. J Biol Chem 276:43111–43121
Acknowledgments
S. Alshalchi was supported by the Institute of International Education and Scholar Rescue. This work was also supported by Research Support Funds Grant (RSFG) from IUPUI and Purdue Research Fund (PRF) from Purdue University to G. Anderson.
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alshalchi, S.A., Anderson, G.G. Expression of the lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis gene lpxD affects biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa . Arch Microbiol 197, 135–145 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-014-1030-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-014-1030-y