Abstract
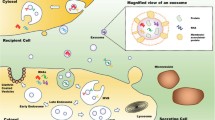
Current cancer diagnostic methods are challenged by low sensitivity, high false positive rate, limited tumor information, uncomfortable or invasive procedures, and high cost. Liquid biopsy that analyzes circulating biomarkers in body fluids represents a promising solution to these challenges. Exosomes are one of the promising cancer biomarkers for liquid biopsy because they are cell-secreted, nano-sized, extracellular vesicles that stably exist in all types of body fluids. Exosomes transfer DNAs, RNAs, proteins, and lipids from parent cells to recipient cells for intercellular communication and play important roles in cancer initiation, progression, and metastasis. Many liquid biopsy biosensors have been developed to offer non- or minimally-invasive, highly sensitive, simple, rapid, and cost-effective cancer diagnostics. This review summarized recent advances of liquid biopsy biosensors with a focus on the detection of exosomal proteins as biomarkers for cancer screening, diagnosis, and prognosis. We reviewed six major types of liquid biopsy biosensors including immunofluorescence biosensor, colorimetric biosensor, surface plasmon resonance (SPR) biosensor, surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) biosensor, electrochemical biosensor, and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) biosensor. We shared our perspectives on future improvement of exosome-based liquid biopsy biosensors to accelerate their clinical translation.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancer Treatment & Survivorship Facts & Figures 2016-2017. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/cancer-treatment-and-survivorship-facts-and-figures/cancer-treatment-and-survivorship-facts-and-figures-2016-2017.pdf.
Aberle DR, Adams AM, Berg CD, Black WC, Clapp JD, Fagerstrom RM, et al. Reduced lung-cancer mortality with low-dose computed tomographic screening. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:395–409. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1102873.
Aberle DR, Abtin F, Brown K. Computed tomography screening for lung cancer: has it finally arrived? Implications of the national lung screening trial. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31(8):1002–8. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2012.43.3110.
Patz EF, Pinsky P, Gatsonis C, Sicks JD, Kramer BS, Tammemägi MC, et al. Overdiagnosis in low-dose computed tomography screening for lung cancer. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:269–74. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.12738.
Chudgar NP, Bucciarelli PR, Jeffries EM, Rizk NP, Park BJ, Adusumilli PS, et al. Results of the national lung cancer screening trial: where are we now? Thorac Surg Clin. 2015;25:145–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thorsurg.2014.11.002.
Church TR, Black WC, Aberle DR, Berg CD, Clingan KL, Duan F, et al. Results of initial low-dose computed tomographic screening for lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:1980–91. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1209120.
Oeffinger KC, Fontham ET, Etzioni R, Herzig A, Michaelson JS, Shih YC, et al. Breast cancer screening for women at average risk: 2015 guideline update from the American Cancer Society. JAMA. 2015;314:1599–614. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2015.12783.
Bray C, Bell LN, Liang H, Collins D, Yale SH. Colorectal cancer screening. WMJ. 2017;116:27–33.
Siravegna G, Marsoni S, Siena S, Bardelli A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14:531–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.14.
Gingras I, Salgado R, Ignatiadis M. Liquid biopsy: will it be the ‘magic tool’ for monitoring response of solid tumors to anticancer therapies. Curr Opin Oncol. 2015;27:560–7. https://doi.org/10.1097/CCO.0000000000000223.
Wan JCM, Massie C, Garcia-Corbacho J, Mouliere F, Brenton JD, Caldas C, et al. Liquid biopsies come of age: towards implementation of circulating tumour DNA. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17:223–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2017.7.
Contreras-Naranjo JC, Wu HJ, Ugaz VM. Microfluidics for exosome isolation and analysis: enabling liquid biopsy for personalized medicine. Lab Chip. 2017;17:3558–77. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7lc00592j.
He M, Zeng Y. Microfluidic exosome analysis toward liquid biopsy for cancer. J Lab Autom. 2016;21:599–608. https://doi.org/10.1177/2211068216651035.
Kowal J, Tkach M, Thery C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2014;29:116–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2014.05.004.
Yanez-Mo M, Siljander PR, Andreu Z, Zavec AB, Borras FE, Buzas EI, et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:27066. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.27066.
Azmi AS, Bao B, Sarkar FH. Exosomes in cancer development, metastasis, and drug resistance: a comprehensive review. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013;32:623–42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-013-9441-9.
Tkach M, Thery C. Communication by extracellular vesicles: where we are and where we need to go. Cell. 2016;164:1226–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.043.
ELA S, Mager I, Breakefield XO, Wood MJ. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12:347–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd3978.
Robbins PD, Morelli AE. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14:195–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3622.
HR M, Bayraktar E, KH G, Abd-Ellah MF, Amero P, Chavez-Reyes A, et al. Exosomes: from garbage bins to promising therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18 https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030538.
Li W, Li C, Zhou T, Liu X, Liu X, Li X, et al. Role of exosomal proteins in cancer diagnosis. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:145. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0706-8.
Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523:177–82. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature14581.
Jakobsen KR, Paulsen BS, Baek R, Varming K, Sorensen BS, Jorgensen MM. Exosomal proteins as potential diagnostic markers in advanced non-small cell lung carcinoma. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26659. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.26659.
Yamashita T, Kamada H, Kanasaki S, Maeda Y, Nagano K, Abe Y, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor localized to exosome membranes as a possible biomarker for lung cancer diagnosis. Pharmazie. 2013;68:969–73. https://doi.org/10.1691/ph.2013.3599.
Clark DJ, Fondrie WE, Yang A, Mao L. Triple SILAC quantitative proteomic analysis reveals differential abundance of cell signaling proteins between normal and lung cancer-derived exosomes. J Proteome. 2016;133:161–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jprot.2015.12.023.
Li XJ, Hayward C, Fong PY, Dominguez M, Hunsucker SW, Lee LW, et al. A blood-based proteomic classifier for the molecular characterization of pulmonary nodules. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:207ra142. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3007013.
Li Y, Zhang Y, Qiu F, Qiu Z. Proteomic identification of exosomal LRG1: a potential urinary biomarker for detecting NSCLC. Electrophoresis. 2011;32:1976–83. https://doi.org/10.1002/elps.201000598.
He M, Crow J, Roth M, Zeng Y, Godwin AK. Integrated immunoisolation and protein analysis of circulating exosomes using microfluidic technology. Lab Chip. 2014;14:3773–80. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4lc00662c.
Zhao Z, Yang Y, Zeng Y, He M. A microfluidic ExoSearch chip for multiplexed exosome detection towards blood-based ovarian cancer diagnosis. Lab Chip. 2016;16:489–96. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5lc01117e.
Yoshioka Y, Kosaka N, Konishi Y, Ohta H, Okamoto H, Sonoda H, et al. Ultra-sensitive liquid biopsy of circulating extracellular vesicles using ExoScreen. Nat Commun. 2014;5:3591. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4591.
Jorgensen M, Baek R, Pedersen S, Sondergaard EK, Kristensen SR, Varming K. Extracellular vesicle (EV) array: microarray capturing of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles for multiplexed phenotyping. J Extracell Vesicles. 2013;2 https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v2i0.20920.
Jorgensen MM, Baek R, Varming K. Potentials and capabilities of the extracellular vesicle (EV) array. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:26048. https://doi.org/10.3402/jev.v4.26048.
Baek R, Jorgensen MM. Multiplexed phenotyping of small extracellular vesicles using protein microarray (EV Array). Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1545:117–27. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6728-58.
Zhang P, He M, Zeng Y. Ultrasensitive microfluidic analysis of circulating exosomes using a nanostructured graphene oxide/polydopamine coating. Lab Chip. 2016;16:3033–42. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6lc00279j.
Liang LG, Kong MQ, Zhou S, Sheng YF, Wang P, Yu T, et al. An integrated double-filtration microfluidic device for isolation, enrichment and quantification of urinary extracellular vesicles for detection of bladder cancer. Sci Rep. 2017;7:46224. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep46224.
Vaidyanathan R, Naghibosadat M, Rauf S, Korbie D, Carrascosa LG, Shiddiky MJ, et al. Detecting exosomes specifically: a multiplexed device based on alternating current electrohydrodynamic induced nanoshearing. Anal Chem. 2014;86:11125–32. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac502082b.
Xia Y, Liu M, Wang L, Yan A, He W, Chen M, et al. A visible and colorimetric aptasensor based on DNA-capped single-walled carbon nanotubes for detection of exosomes. Biosens Bioelectron. 2017;92:8–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.01.063.
Sina AA, Vaidyanathan R, Dey S, Carrascosa LG, Shiddiky MJ, Trau M. Real time and label free profiling of clinically relevant exosomes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:30460. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep30460.
Zhu L, Wang K, Cui J, Liu H, Bu X, Ma H, et al. Label-free quantitative detection of tumor-derived exosomes through surface plasmon resonance imaging. Anal Chem. 2014;86:8857–64. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac5023056.
Im H, Shao H, Park YI, Peterson VM, Castro CM, Weissleder R, et al. Label-free detection and molecular profiling of exosomes with a nano-plasmonic sensor. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32(5):490–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2886.
Zong S, Wang L, Chen C, Lu J, Zhu D, Zhang Y, et al. Facile detection of tumor-derived exosomes using magnetic nanobeads and SERS nanoprobes. Anal Methods. 2016;8:5001–8. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ay00406g.
Wei F, Yang J, Wong DT. Detection of exosomal biomarker by electric field-induced release and measurement (EFIRM). Biosens Bioelectron. 2013;44:115–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.12.046.
Jeong S, Park J, Pathania D, Castro CM, Weissleder R, Lee H. Integrated magneto-electrochemical sensor for exosome analysis. ACS Nano. 2016;10:1802–9. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.5b07584.
Doldan X, Fagundez P, Cayota A, Laiz J, Tosar JP. Electrochemical sandwich immunosensor for determination of exosomes based on surface marker-mediated signal amplification. Anal Chem. 2016;88:10466–73. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02421.
Zhou Q, Rahimian A, Son K, Shin DS, Patel T, Revzin A. Development of an aptasensor for electrochemical detection of exosomes. Methods. 2016;97:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.10.012.
Shao H, Chung J, Balaj L, Charest A, Bigner DD, Carter BS, et al. Protein typing of circulating microvesicles allows real-time monitoring of glioblastoma therapy. Nat Med. 2012;18:1835–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2994.
Fang S, Tian H, Li X, Jin D, Li X, Kong J, et al. Clinical application of a microfluidic chip for immunocapture and quantification of circulating exosomes to assist breast cancer diagnosis and molecular classification. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0175050. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175050.
Singh P. SPR biosensors: historical perspectives and current challenges. Sensors Actuators B Chem. 2016;229:110–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.118.
Rupert DL, Lasser C, Eldh M, Block S, Zhdanov VP, Lotvall JO, et al. Determination of exosome concentration in solution using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 2014;86:5929–36. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500931f.
Grasso L, Wyss R, Weidenauer L, Thampi A, Demurtas D, Prudent M, et al. Molecular screening of cancer-derived exosomes by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407:5425–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-8711-5.
Homola J. Surface plasmon resonance sensors for detection of chemical and biological species. Chem Rev. 2008;108:462–93. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068107d.
Stewart ME, Anderton CR, Thompson LB, Maria J, Gray SK, Rogers JA, et al. Nanostructured plasmonic sensors. Chem Rev. 2008;108:494–521. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr068126n.
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van Duyne RP. Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater. 2008;7:442–53. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2162.
Im H, Shao H, Weissleder R, Castro CM, Lee H. Nano-plasmonic exosome diagnostics. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015;15:725–33. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737159.2015.1041378.
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge the funding support from National Cancer Institute of the National Institutes of Health under award number 5R33CA191245. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest Editors: Juliane Nguyen and Steven Jay
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Yang, Y. & Wu, Y. Recent Advances in Exosomal Protein Detection Via Liquid Biopsy Biosensors for Cancer Screening, Diagnosis, and Prognosis. AAPS J 20, 41 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-018-0201-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-018-0201-1